Video 3D Animation:
Observe closely the oscillation. Initially , the system is static. Then I have given a disturbance to the system by pulling on the mass and releasing it. The oscillation starts as a Simple Harmonic Motion. It will continue for ever if there is no friction between the mass and ground (the baseplate).
Hence, there arise some physics Assumptions behind the animation and subsequent equations derived in next few lessons. These are :
- there is zero friction between the mass and ground
- the spring is massless (this ensures that the spring itself doesn’t have its own inertia)
- the block is a point mass (this makes the equations simpler)
- and the ground is stationary on which the mass is sliding (i.e. the baseplate on which the whole system is working). This makes things simpler . It becomes an inertial frame of reference, for an oberver like us standing outside the frame, instead of a complicated Non-inertial frame of reference if the baseplate itself was accelerating.
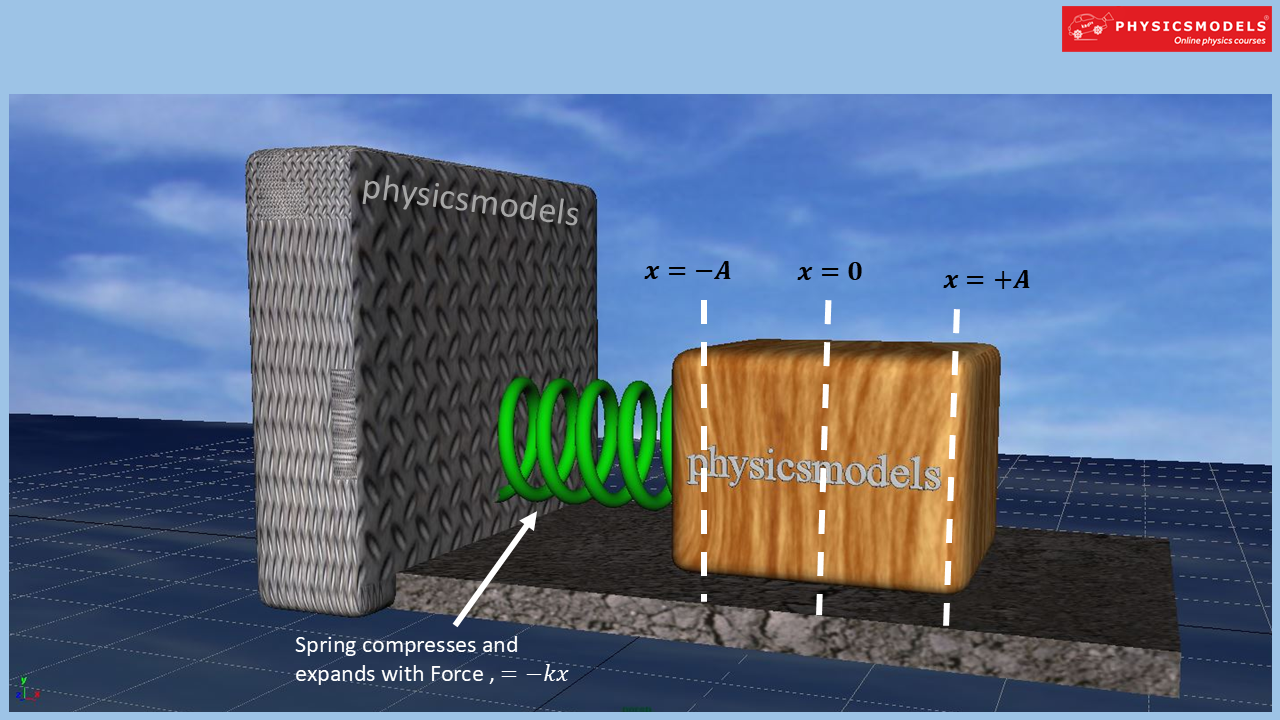
Below is a snapshot that starts giving you an idea of Mean Position, and Amplitude of oscillation on both sides of the Mean Position. Hence the Max Amplitude is described as +/- A . The Amplitude is a variable ‘x’ with time, where x changes from x =0 to x=+A and x= -A
Velocity is a derivation of dx/dt, the Rate of change of Displacement with respect to time.
Above, a Block,is pulled by us manually and rekeased. The Block and Spring together behave as a SYSTEM, and start oscillating to & fro. This can go on for a very long time, if there is ZERO friction between the Block and the ground.
If there is Friction existing between the Block and Ground, the block will come to a stop after a few oscillations, this will then be called Damped Oscillations.
Now let’s come back to SHM – Simple Harmonic Motion.
Question: Is there a big difference between Harmonic Motion and Simple Harmonic motion ?
Yes, absolutely, and this must be clearly understood.
Harmonic motion
- is any periodic motion
- example Earth rotating around the Sun, or Moon rotating around the Earth. But there is no Equilibrium position or Mean position where the Earth or Moon returns in their motion.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
- is a motion where there is a Restoring force , meaning some Force which brings back the object to its Mean position or Equilibrium position. The Force must be directly proportional to displacement from Equilibrium position (or Mean Position), creating a perfect sinusoidal wave, then only the condition is satisfied for SHM
Several real-life things like springs, pendulums, even waves follow Simple Harmonic Motion. In this course, you can see repeatedly in slow motion, our Animations and Video explanations to get the concepts and equations clear.
1) Introduction: what is Simple Harmonic Motion
Read about Restoring Force and its equation.
2) Displacement, Velocity, and acceleration : the mysterious connection between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple harmonic Motion
3) Simple Pendulum and its equations
4) Simple harmonic motion: Spring and Mass System
5) SHM : case of a single spring connecting two blocks oscillating on a flat Horizontal Plane
6) Damped Harmonic Motion concept : wave damping
7) Damped Oscillations : Equations — Amplitude reduction with time
8) Solved problems
Course Features
- Lectures 10
- Quiz 1
- Duration Lifetime access
- Skill level All levels
- Language English
- Students 210
- Certificate No
- Assessments Yes
- 1 Section
- 10 Lessons
- Lifetime
- Simple Harmonic Motion11
- 1.1Introduction- Simple Harmonic Motion, different from Harmonic Motion
- 1.2Spring-Mass System – vertical arrangement
- 1.3Conditions for SHM
- 1.4Equations->Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration, Kinetic and Potential Energy
- 1.5Simple Pendulum
- 1.6Spring-mass system- Horizontal arrangement- Understand displacement, velocity and Total Energy derivation
- 1.7SHM – System of Two Masses conected by a single Spring, and Practical Applications
- 1.8Damped Oscillations and Practical Applications
- 1.9Equations – Damped oscillation
- 1.10Simple Harmonic Motion – Solved problems
- 1.11Simple Harmonic Motion-Theory Test42 Minutes14 Questions